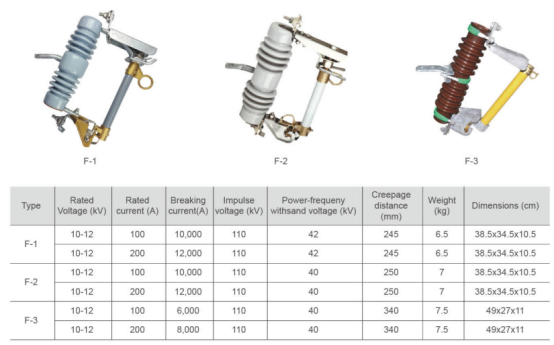
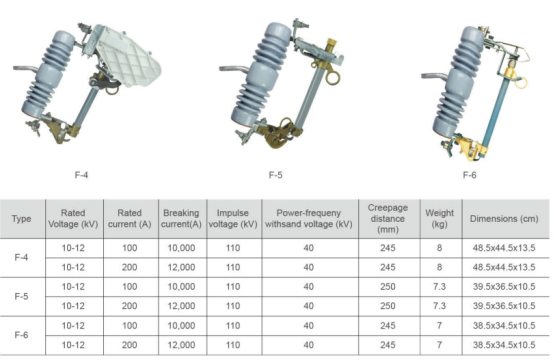
High voltage drop type fuse
Short Description:
Drop out fuses are suitable for power systems with a frequency of 50Hz and a rated voltage of 35KV and below, installed on the high voltage side of distribution transformers or on the main lines of distribution. The main functions include areas with low requirements for protection performance, which can be used in conjunction with isolation switches to replace automatic air switches; It can also be used in conjunction with load switches to replace expensive circuit breakers. It also has short-circuit protection, overload and isolation circuits.
Product details
Product overview:
Drop out fuses are suitable for power systems with a frequency of 50Hz and a rated voltage of 35KV and below, installed on the high voltage side of distribution transformers or on the main lines of distribution. The main functions include areas with low requirements for protection performance, which can be used in conjunction with isolation switches to replace automatic air switches; It can also be used in conjunction with load switches to replace expensive circuit breakers. It also has short-circuit protection, overload and isolation circuits.
Working principle:
The load drop fuse has added elastic auxiliary contacts and arc extinguishing covers to switch the load current. When a drop out fuse operates normally, the fuse tube is tensioned by the fuse to form a closed position. When the system malfunctions, the fault current causes the fuse to quickly melt and form an arc. The arc extinguishing tube is heated by the arc and decomposes a large amount of gas, creating high pressure inside the tube and strongly blowing along the pipeline. The arc is quickly stretched and extinguished. After the fuse is blown, the lower static contact loses tension and flips down, causing the tightening mechanism to release the fuse tube, and the fuse tube falls to form a clear breaking position. When a load needs to be pulled, use an insulating rod to pull the contact, while the active and stationary contacts are still in contact. Continue to pull the contact with the insulating rod, and the auxiliary contacts also separate, generating an arc between the heads. The arc is elongated in the narrow slot of the arc extinguishing cover, and gas is generated in the arc extinguishing cover. When the current flows through zero, the arc is extinguished.
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS:
1. Fuses should be installed vertically to prevent arcs from flying onto adjacent live parts.
2. The fuse and the fixed contact should make a straight and non tilted contact.
3. For drop out fuses, the axis of the fuse tube should be at an angle of 15-30 ° to the plumb line, and the rotating part should be flexible. When dropped, it should not collide with other objects.
4. The specifications of the fuse should meet the design requirements, and there should be no bending, flattening or damage. The fuse and contact should be tightly and firmly pressed.
5. The rated current of the fuse and the fuse (wire or piece) must be indicated on the fuse, and the capacity of the fuse should meet the requirements of the protected electrical appliance. Fuses that have not been verified or have no rated current indication are not allowed to be used.
Operation usage